On August 3, 2021, the Seventy-Fourth World Health Assembly adopted the Global Patient Safety Action Plan 2021–2030.1 The 2021 decision to adopt the action plan followed the May 2019 World Health Assembly’s mandate to develop a global patient safety action plan.
The Global Patient Safety Action Plan 2021–2030 was developed by the Integrated Health Services WHO team in consultation with WHO Member States and relevant stakeholders. The aim is to provide strategic direction and an action-oriented framework to facilitate the implementation of strategic patient safety interventions at all levels of health systems globally over the next 10 years (2021–2030).2
The action plan includes the following seven strategic objectives:
- Policies to eliminate avoidable harm in health care: Make zero avoidable harm to patients a state of mind and a rule of engagement in the planning and delivery of health care everywhere
- High-reliability systems: Build high-reliability health systems and health organizations that protect patients daily from harm
- Safety of clinical processes: Ensure the safety of every clinical process
- Patient and family engagement: Engage and empower patients and families to help support the journey to safer health care
- Health worker education, skill, and safety: Inspire, educate, and protect health workers in order to contribute to the design and delivery of safe care systems
- Information research and risk management: Ensure a constant flow of information and knowledge to drive the mitigation of risk, reduction in levels of avoidable harm, and improvements in the safety of care
- Synergy, partnership, and solidarity: Develop and sustain multisectoral and multinational synergy, partnership, and solidarity to improve patient safety and quality of care
To achieve these objectives, 35 specific strategies have been identified. Figure 1 depicts the 7×5 matrix for the action framework. In addition, 10 core indicators to measure and report progress on implementing the global action plan are proposed. Table 1 lists the 10 core indicators for monitoring progress on the seven strategic objectives. The WHO secretariat plans to monitor the achievement of these indicators at the global, regional, and national levels. For each core indicator, the global targets for achievement by 2023, 2025, 2027, and 2030 are specified. Furthermore, advanced indicators for each strategic objective are proposed for countries to monitor as applicable to their context, capacity, and patient safety priorities.
The action plan acknowledges the diversity in structure, funding, and governance of health care systems worldwide and the fact that full implementation at the national level will be a long-term agenda. The following key implementation milestones are suggested:
- Milestone 1: Assess the landscape
- Milestone 2: Secure strong commitment from political and organizational leadership
- Milestone 3: Establish a sustainable mechanism for implementation
- Milestone 4: Align with national context and priorities
- Milestone 5: Decide on and design the model of change for implementation
The World Health Assembly’s director-general will report back to the WHO every 2 years on the progress made in implementing the plan, starting in 2023 and continuing until 2031.1
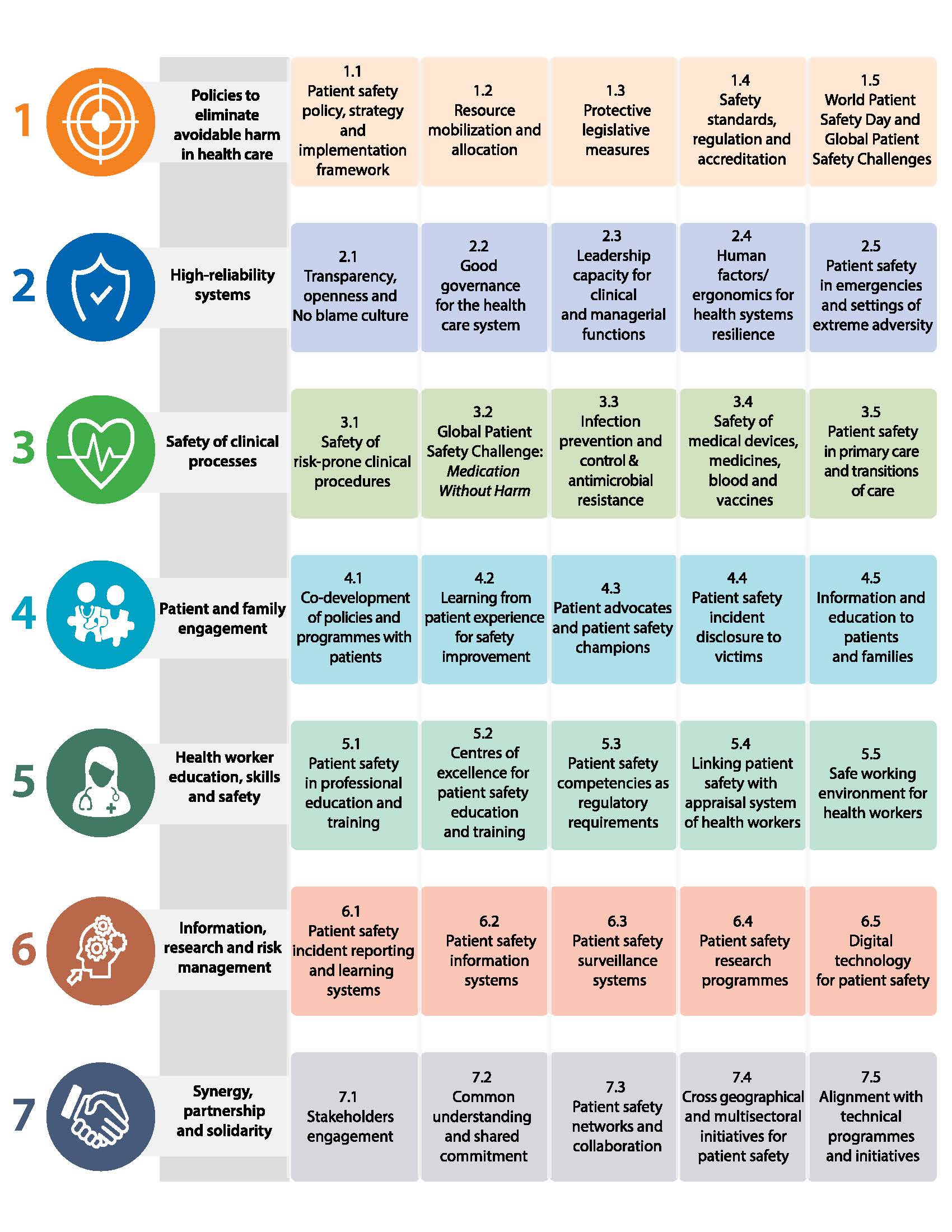
Figure 1. 7×5 matrix for the action framework.
Table 1. Global Patient Safety Action Plan 2021–2030 Strategic Objectives and Core Indicators
|
Strategic Objective
|
Core Indicator(s)
|
|
Strategic Objective 1. Make zero avoidable harm to patients a state of mind and a rule of engagement in the planning and delivery of health care everywhere
|
1. Number of countries that have developed a national action plan (or equivalent) for implementing patient safety policy and strategies
|
|
Strategic Objective 2. Build high-reliability health systems and health organizations that protect patients daily from harm
|
2. Number of countries that have implemented a system for reporting never events (or sentinel events)
|
|
Strategic Objective 3. Ensure the safety of every clinical process
|
3. Significant reduction in health care–associated infections
4. Significant reduction in medication-related harm (adverse drug events)
|
|
Strategic Objective 4. Engage and empower patients and families to help and support the journey to safer health care
|
5. Number of countries that have a patient representative on the governing board (or an equivalent mechanism) in 60% or more hospitals
|
|
Strategic Objective 5. Inspire, educate, and protect health workers in order to contribute to the design and delivery of safe care systems
|
6. Number of countries that have incorporated a patient safety curriculum in education programs or courses for health care professionals
7. Number of countries that have signed up for implementation of WHO Health Worker Safety Charter
|
|
Strategic Objective 6. Ensure a constant flow of information and knowledge to drive the mitigation of risk, reduction in levels of avoidable harm, and improvements in the safety of care
|
8. Number of countries that have 60% or more health care facilities participating in a patient safety incident report and learning system
9. Number of countries that publish an annual report on patient safety
|
|
Strategic Objective 7. Develop and sustain multisectoral and multinational synergy, partnership, and solidarity to improve patient safety and quality of care
|
10. Number of countries that have established a national patient safety network
|
- World Health Organization (WHO). Seventy-Fourth World Health Assembly. Decision WHA74(13). May 31, 2021. Global Action on Patient Safety. Available at https://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/WHA74/A74(13)-en.pdf. Accessed August 26, 2021.
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Patient Safety Action Plan 2021–2030: Towards Eliminating Avoidable Harm in Health Care. Geneva: WHO, 2021. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. Available at www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240032705. Accessed August 26, 2021.